3 Pixel - Your eye perceives Continuity
Digital Graphic / image
1 Graphics
2 Pixel
“Picture Element”
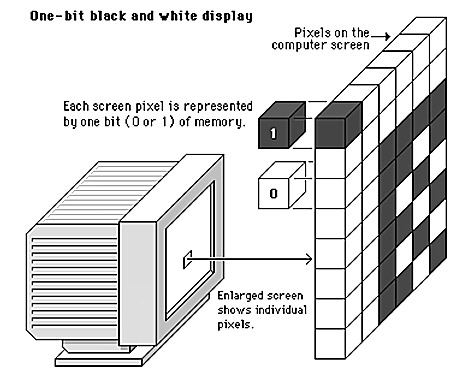
On a screen, the smallest part of an image is called a “pixel”
Pixels are just those squalling of dots that make up an on-screen image

3 Pixel - Your eye perceives Continuity

4 Pixel - Your eye perceives Continuity

5 Zoom-In on the Patch

6 Resolution
Resolution is how fine the detail is on a screen or printout.
Types of Resolution
Monitor resolution
Image resolution
Bit resolution
Printer resolution
7 MonitorResolution
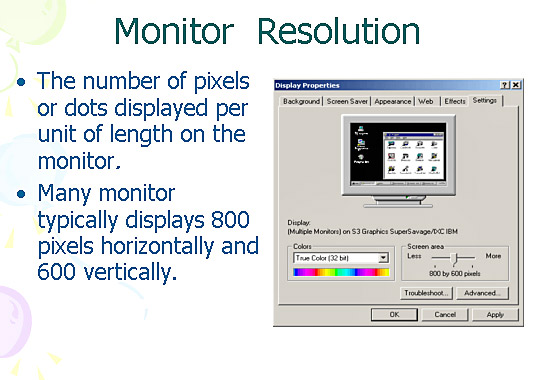
The number of pixels or dots displayed per unit of length on the monitor.
Many monitor typically displays 800 pixels horizontally and 600 vertically.
8 Monitor Resolution
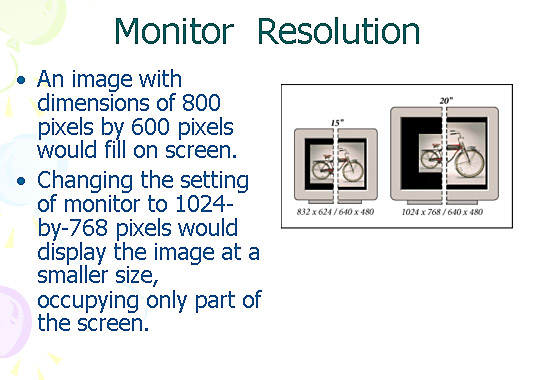
An image with dimensions of 800 pixels by 600 pixels would fill on screen.
Changing the setting of monitor to 1024-by-768 pixels would display the image
at a smaller size, occupying only part of the screen.
9 Image Resolution
The number of pixels displayed per unit of printed length in an image.
Measured in pixels per inch (ppi) or dots per inch (dpi)
The web is always 72dpi - this is the standard resolution of a monitor.
Higher the resolution, more pixels in the image
10 Example of an image at 72-ppi and 300-ppi
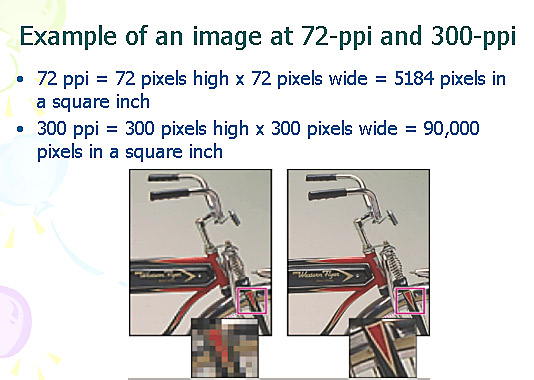
72 ppi = 72 pixels high x 72 pixels wide = 5184 pixels in a square inch
300 ppi = 300 pixels high x 300 pixels wide = 90,000 pixels in a square inch
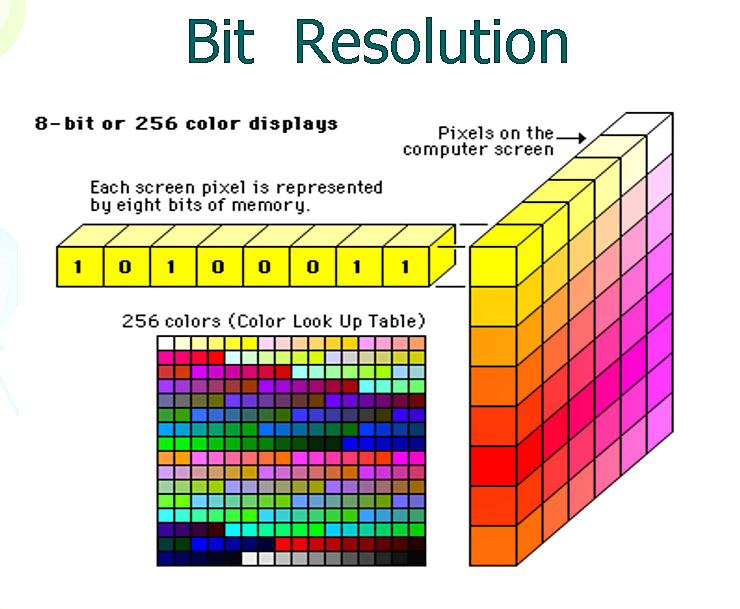
11 Bit Resolution
Measurement of the number of bits of stored information per pixel.
Determines how much color information is available for each pixel
12 Bit Resolution
13 Bit Depth
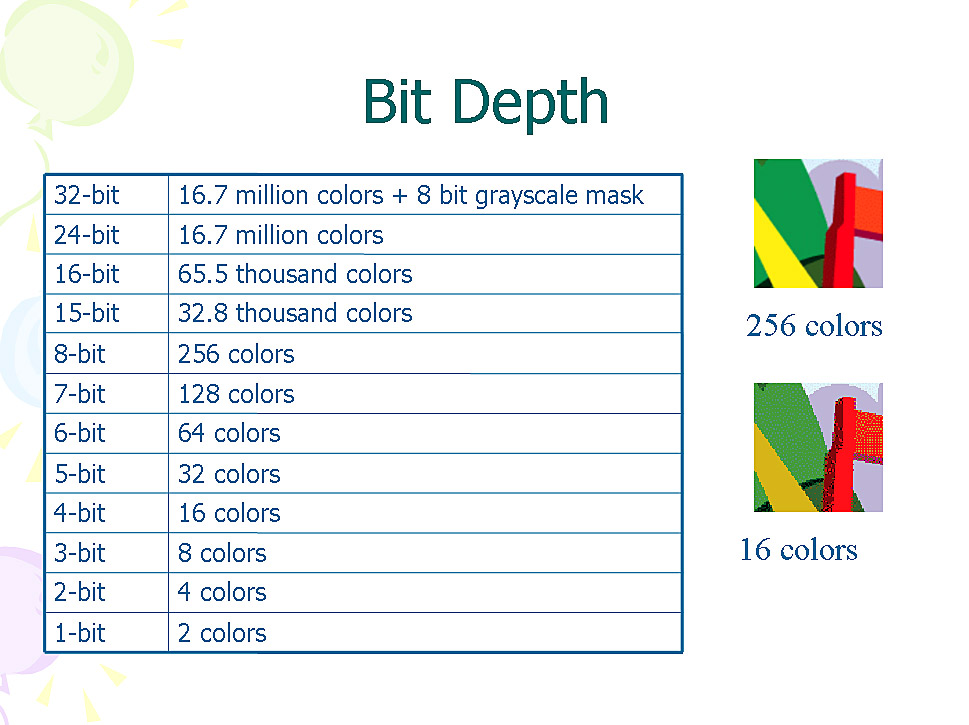
14 Bit depth drastically affects file size

15 Printer Resolution
The number of ink dots per inch (dpi) produced by all printers, including imagesetters.
Most desktop printers have a resolution of 300 to 720 dpi.
16 File Size
The digital size of an image, measured in kilobytes (K), megabytes (MB), or
gigabytes (GB).
The file size of an image is proportional to its resolution
Images with high resolution have greater detail and result in higher file sizes.
Web graphics only need to be 72 dpi (monitor resolution).
Photoshop supports a maximum file size of 2 GB and maximum pixel dimensions
of 30,000 by 30,000 pixels per image.
17 Color Mode
A color mode determines the color model used to display and print images.
Common models include
RGB (red, green, blue)
CMYK (cyan, magenta, yellow, black)
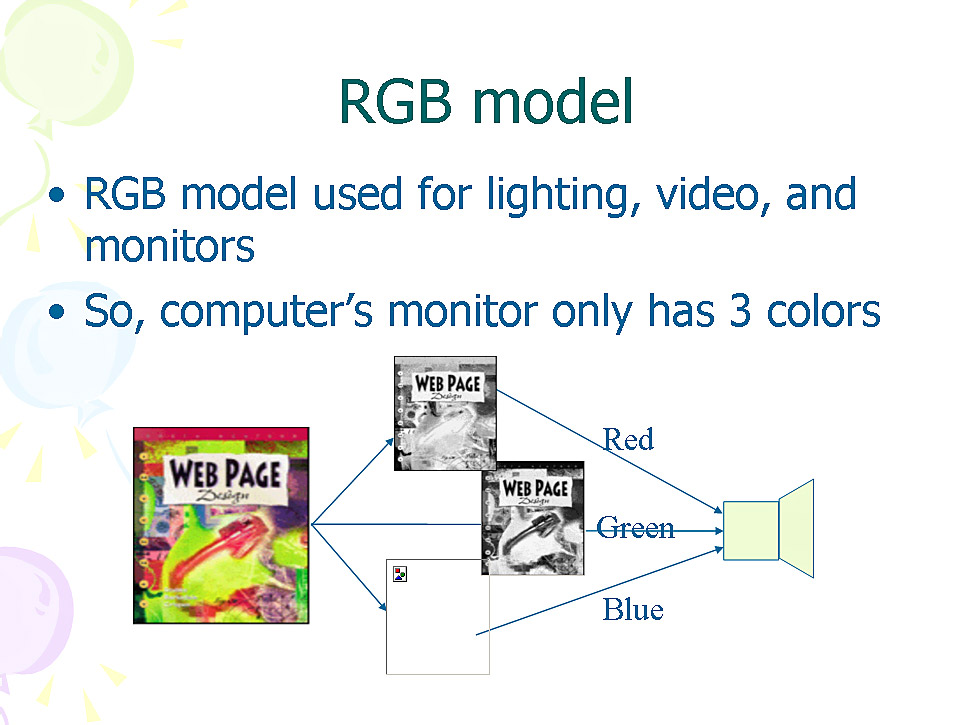
18 RGB model
RGB model used for lighting, video, and monitors
So, computer’s monitor only has 3 colors
19 CMYK model
The CMYK model is based on the light-absorbing quality of ink printed on paper.

20
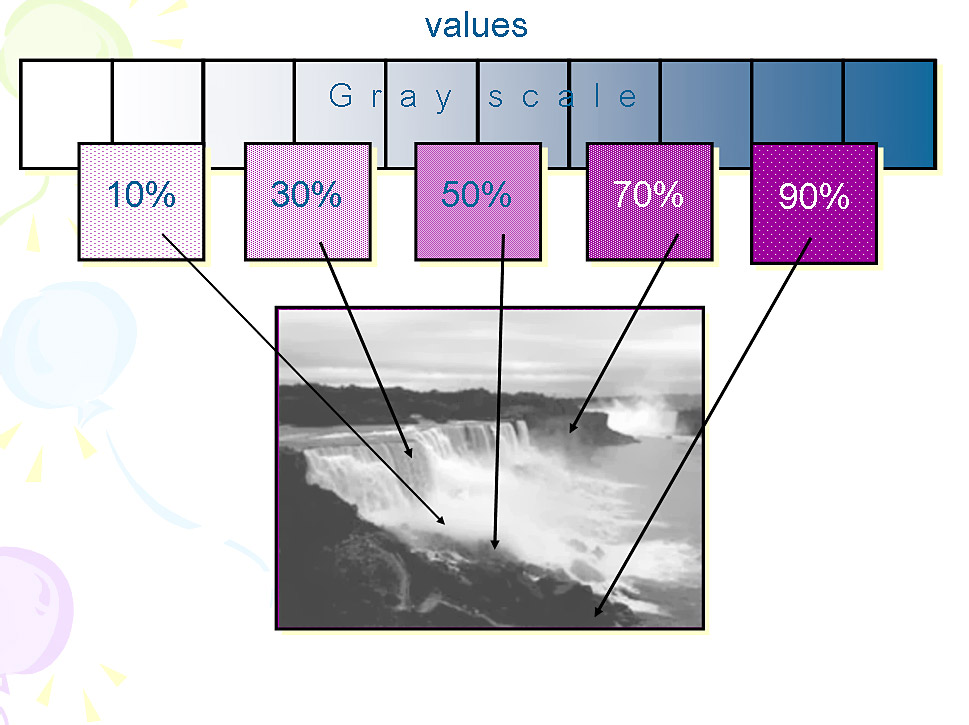
21
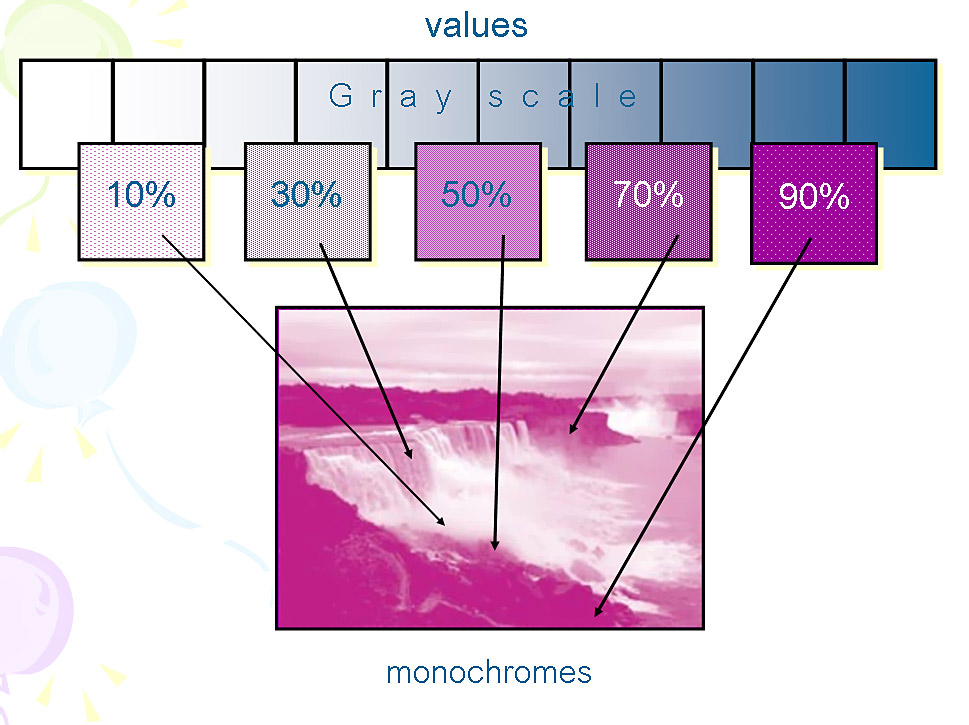
22
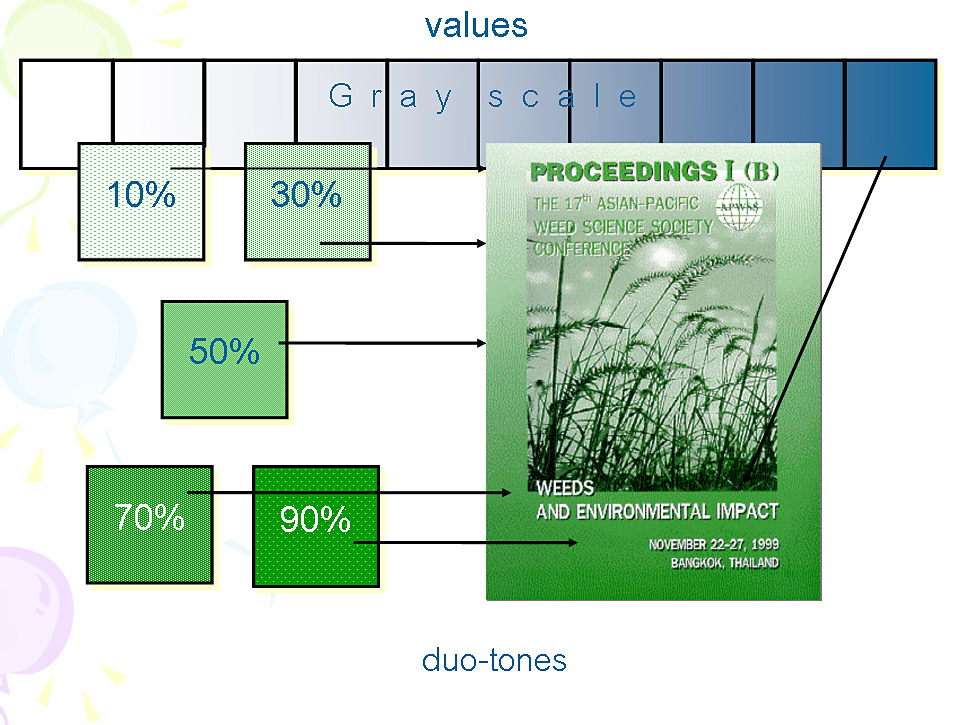
23 Graphic formats
True Image Formats
Accurately stores an image for future editing
Hundreds of true image formats including: .tif, .bmp, .pict, .psd
No compression involved
Web Image Formats
GIF
JPEG
PNG
24 JPEG
Joint Photographic Experts Group
A universal standard for the digital compression and decompression of still
images for use in computer systems
Can store millions of colors (16,777,216 colors)
File format used for photographic images, continuous tone images.
Doesn't work well for line art and images with large blocks of color
25 JPEG File Format
When you save a file as a .jpg you have the option of saving it as a low, medium, high, or maximum quality.
26 Progressive JPEG
Low to high resolution

27 GIF
Graphics Interchange Format
An extension for graphic files in a format developed by CompuServe
Used for line art and images with large blocks of color or 256 colors
Works best for flat color, sharp-edged art (stuff that looks like clip art),
diagrams, text, ….
Doesn't work well for highly detailed images: Photographs.
28 GIF
29 GIF vs JPEGGIFs
256 Colors
Best for flat-color art
Transparent
Interlaced
Animation
JPEGs
16,777,216 colors
Best for full-color images of real-world scenes
No transparent, animation
Progressive
30 GIF vs JPEG
31 GIF vs JPEG
32 GIF or JPEG?
33 GIF89 format
GIF have 2 varieties
GIF87 …. Normal GIF
GIF89a
Interlaced GIF
Transparent GIF
Animation GIF
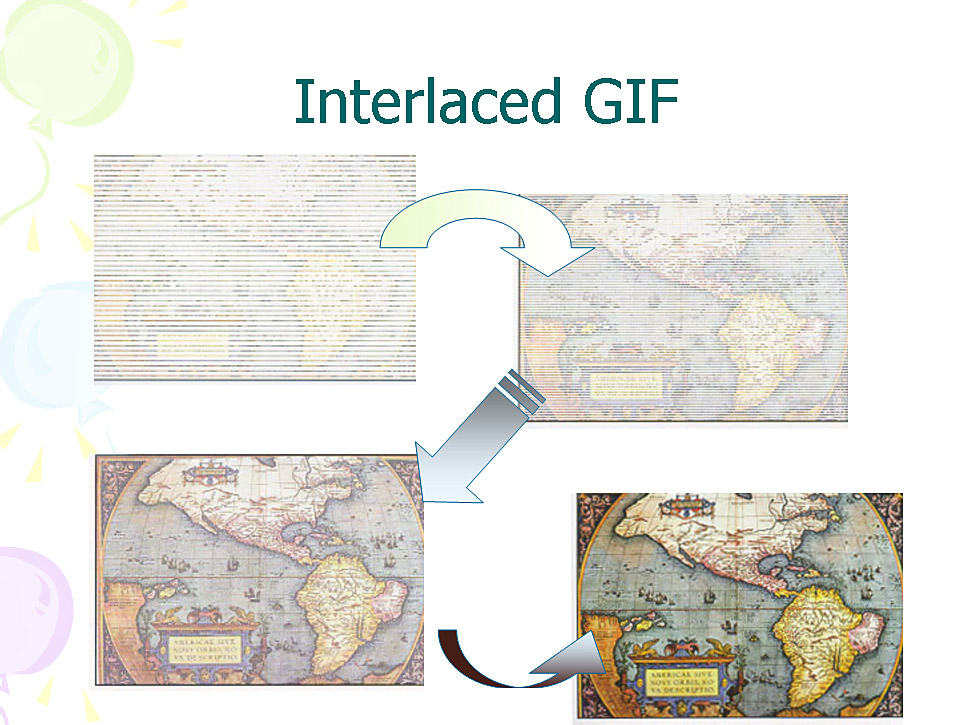
34 Interlaced GIF
affects display of image when loading
image displays as series of lines building up to whole picture
gives ‘venetian blind’ effect (depends on browser)
good for larger images
gives good idea of what image represents without waiting for all image to be
loaded
35 Interlaced GIF
36 Transparent GIF
scan set a colour to be invisible
set background to transparent

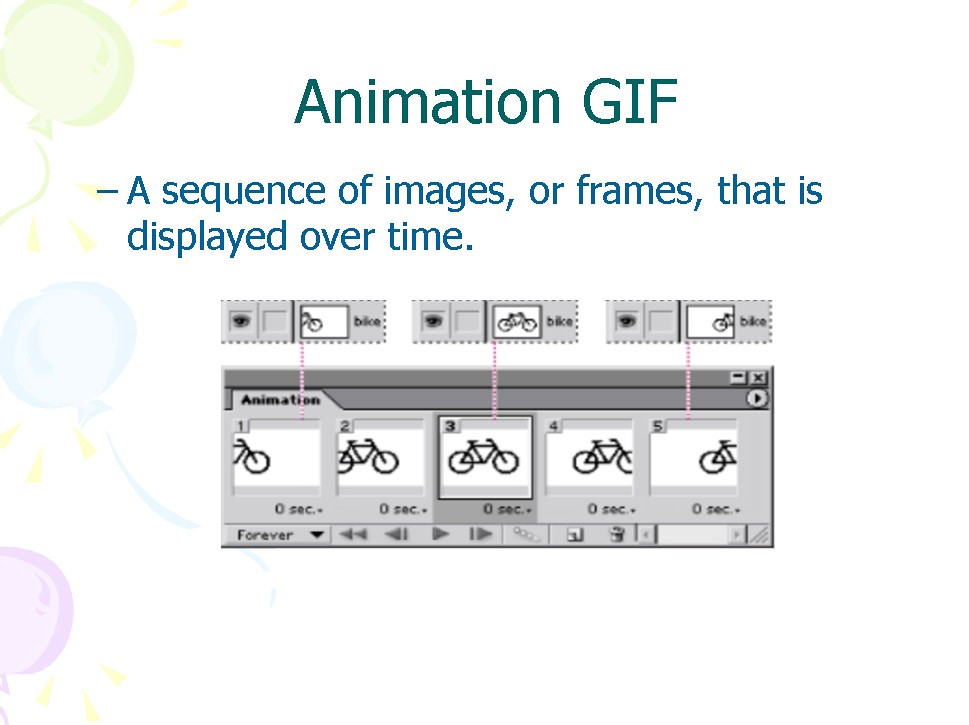
37 Animation GIF
A sequence of images, or frames, that is displayed over time.
38 PNG
Portable Network Graphics format
24-bit color support
Capability for interlacing and transparency
Compression which works equally well for photographs and logos
39 Image file
Original Image File
Have layer in the file
Can editing, deleting
File extension is .psd
Working Image File
Have only one layer
Can’t editing, deleting
File extension is .jpg, .gif or .png